Gum treatment is the treatment of active gum and jaw bone disease. The treatment can slow or stop the progression of the disease. Since there are different stages of gum disease (from gingivitis to advanced periodontitis), there are different levels of treatment. In some cases, the patient may be referred to a specialist.
Gum treatment consists of one or more of the following procedures, depending on the individual case:
Prophylaxis(Cleaning)
Scaling and Root Planing
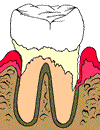 |
Scaling and Root Planing is a common non-surgical treatment for periodontal disease. By using special instruments, we remove bacteria and infection from the unhealthy deep pockets around the teeth below the gum line. This is often referred to as a "deep cleaning". |
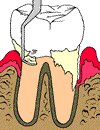
| First the tooth is scaled to remove the plaque and tarter that has accumulated on the tooth. |
 |
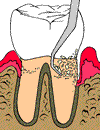 |
Then the root is planed or smoothed. This eliminates any rough areas on the root that can easily trap plaque and bacteria. |
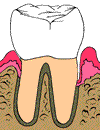
A smooth clean root provides a healthy environment to
allow the gums to heal naturally and reattach to the
tooth. This will create a reduced pocket, therefore
eliminating areas for bacteria to hide and cause further
disease.
Scaling and Root Planing combined with a strict home care routine and more frequent periodontal cleanings and exams will increase your chances of keeping your natural smile.
Gum Surgery
Sometimes, in order to treat advanced gum disease, surgical procedures are necessary, such as:
- Crown Lengthening
- Pocket Depth Reduction
- Soft Tissue Grafts
- Bone and Tissue Regeneration
- Ridge Augmentation
Advanced Medications
 Recent advances in periodontal treatment allow
us to now place medications directly at the site
of infection. One of the most commonly used medications
of this kind is Arestin™.
Another medication that we sometimes use is Atridox™. These are often used in conjunction with scaling and
root planing. In addition, an antimicrobial rinse
such as Chlorhexidine is sometimes used after some procedures. Recent advances in periodontal treatment allow
us to now place medications directly at the site
of infection. One of the most commonly used medications
of this kind is Arestin™.
Another medication that we sometimes use is Atridox™. These are often used in conjunction with scaling and
root planing. In addition, an antimicrobial rinse
such as Chlorhexidine is sometimes used after some procedures.  |
Strict Home Care Regimen
A home care routine specific to the patient's individual needs may be prepared to prevent the patient from relapsing.







